
Compliance Regulations by Industry A Practical Guide
Welcome to the new era of compliance. It's a complex world, and now more than ever, getting it right is non-negotiable. Understanding compliance regulations by industry is a lot like learning the rules for different sports—what's a legal move in basketball is a major penalty in soccer. This guide will serve as your roadmap to the specific rules of your game, with a special focus on the seismic shifts being driven by new laws like the EU AI Act.
Why Compliance Rules Are Not One Size Fits All
Trying to navigate the world of compliance can feel like a maze. Every industry has its own unique pressures, risks, and public expectations, which is why regulations are so carefully tailored.
Think about it this way: a chef follows incredibly strict health and safety codes to prevent foodborne illness, while a construction foreman follows rigorous building codes to make sure a skyscraper doesn't fall down. Both are laser-focused on compliance, but they are reading from completely different playbooks.
This sector-specific approach is crucial because the consequences of a mistake can be so vastly different. A compliance slip-up in finance could trigger market instability or massive fraud. In healthcare, that same slip-up could put patient safety at risk or expose highly sensitive medical data. The rules are there to protect what's most vulnerable in each field.
The Shifting Regulatory Landscape
What adds another wrinkle to this is the sheer speed of technology. Innovations in AI, data analytics, and digital communication are forcing regulators to constantly rewrite the rulebook. What was considered a best practice just a year or two ago might be the bare minimum requirement today. Staying ahead is a real challenge.
This constant evolution is being pushed by a few key forces:
- Data Proliferation: Companies are gathering and analyzing mind-boggling amounts of data, which has led directly to tougher privacy laws.
- Global Interconnectivity: A new regulation in one part of the world can create ripples that affect business operations across the globe.
- Emerging Technologies: New tools like generative AI create new risks—risks that old laws were never built to handle.
The Rise of AI and the EU AI Act
Perhaps the biggest game-changer on the horizon is the regulation of artificial intelligence. The European Union's AI Act is a groundbreaking piece of legislation that's setting the global standard for how AI is built, used, and watched over. It establishes a risk-based framework that sorts AI tools into different tiers, each with its own level of required oversight.
The EU AI Act isn't just a European concern. Its rules apply to any company offering AI services to people in the EU, no matter where that company is located. This makes understanding it a global necessity.
This law touches almost every industry you can think of, from the AI models that decide on credit scores in banking to the diagnostic tools helping doctors in hospitals. As new technologies become fundamental to how we do business, specialized platforms are popping up to help companies manage these complex new rules. For any organization working on this frontier, figuring out how to comply with the AI Act is the essential first move in building a compliance strategy that can stand the test of time.
The Universal Pillars of Modern Compliance

Before we dive into the specific compliance regulations by industry, we need to get a handle on the ground rules that apply to pretty much everyone. Think of the modern compliance landscape as a massive building. Each floor—whether it's finance, healthcare, or tech—has its own unique layout and function. But the entire structure is held up by two non-negotiable pillars: data privacy and Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG).
These two areas aren't just nice-to-haves or niche concerns anymore. They’ve become fundamental expectations for any serious business, regardless of what you sell or who you serve. Getting these right provides the baseline you need to tackle the more specialized rules that will pop up in your specific industry. One pillar dictates how you handle information, and the other defines how you interact with the world around you.
The Data Privacy Mandate
Data is the new oil, the lifeblood of the modern economy. That makes protecting it an absolute, non-negotiable responsibility. The Wild West days of treating personal information like a free-for-all commodity are long gone. Landmark regulations have set a new global standard where safeguarding data isn't just good practice—it's a requirement for doing business at all.
This shift has pushed data privacy and cybersecurity to the top of the compliance agenda in every major market. If your company touches data from EU citizens, for example, you have to play by the rules of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which enforces strict protocols on data handling and breach notifications. In the U.S., laws like the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) give people significant power over their personal information, creating a heavy lift for businesses. You can find more details on these and other upcoming regulations in these 2025 corporate law requirements on ceb.com.
The core idea is simple: individuals own their data. Your organization is just its temporary guardian. This philosophy has created a common set of requirements you'll see in nearly every data privacy law.
- Transparency: You must be crystal clear with users about what data you collect and why.
- Consent: You need to get explicit, opt-in permission before you process someone's personal information.
- User Rights: People need an easy way to see, correct, or delete the data you hold on them.
- Security: You are responsible for implementing tough security measures to keep that data safe from breaches and prying eyes.
These principles are the bedrock of digital trust. Get them wrong, and you're not just looking at massive fines. You’re risking the kind of reputational damage that can be impossible to repair.
The Rise of ESG as a Core Business Function
The second pillar, Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG), has made a surprisingly fast journey from the corporate fringe to the center stage. What was once seen as a simple matter of corporate social responsibility is now a critical part of risk management, strategic planning, and, of course, regulatory compliance. Everyone is finally acknowledging that a company's long-term health is tied directly to its environmental footprint, its social impact, and its internal ethics.
ESG is no longer just about public perception; it's about operational resilience and financial viability. Regulators, investors, and consumers now demand tangible proof of a company's commitment to sustainable and ethical practices.
This has introduced a whole new set of compliance demands that cut across every industry. Companies are now being required to report on specific ESG metrics, proving they are accountable in three key areas.
- Environmental: This is all about tracking and reporting carbon emissions, managing waste responsibly, and assessing how climate-related risks could impact your operations.
- Social: This bucket covers everything from fair labor practices and supply chain ethics to data privacy and your relationship with employees and local communities.
- Governance: This zeroes in on board oversight, executive pay, shareholder rights, and the internal controls that prevent corruption and keep things ethical.
Together, data privacy and ESG form the universal foundation of compliance today. Understanding them is your first and most important step toward successfully navigating the specific rules of your own sector.
High Stakes and Tight Scrutiny in Financial Services

The financial services sector operates under a microscope. It’s an industry built entirely on trust, where one misstep can cause market panic, wipe out a family’s life savings, or inadvertently fund criminal enterprises. Because the stakes are so incredibly high, the web of compliance regulations by industry is arguably the most tangled and dense right here. These rules are all designed to do one thing: keep the system stable, transparent, and fair.
Think of the global financial system as a high-pressure, high-volume plumbing network, with trillions of dollars zipping through its pipes every single day. The regulations are the sophisticated valves, filters, and gauges that keep the whole thing from bursting. They're there to stop contamination (like dirty money), block illegal flows, and ensure the pressure is stable for everyone connected to it.
Core Regulations Preventing Financial Crime
If you work in finance, you live and breathe two key regulations: Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX). They tackle different problems, but both are absolutely critical for maintaining the integrity of the financial system.
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) rules are the industry’s front line against crime. These aren't just suggestions; they are mandates that force banks and other firms to actively hunt for and report suspicious activity. In a way, financial institutions are deputized to spot transactions that could be tied to terrorism, drug trafficking, or other illegal ventures.
It's a constant state of vigilance. For example, if a client with a predictable income suddenly starts making huge, irregular cash deposits, AML systems will throw up a red flag. The institution then has a legal duty to investigate and, if necessary, file a Suspicious Activity Report (SAR) with agencies like the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN).
Ensuring Corporate Accountability with SOX
The Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX), on the other hand, was born out of scandal. Passed in the wake of massive accounting frauds in the early 2000s, SOX is all about protecting investors by demanding rock-solid accuracy in corporate financial reporting. It puts senior executives on the hook personally, forcing them to certify that their company’s financial statements are true.
SOX was a game-changer for corporate governance because it made accountability personal. Executives at the top can no longer plead ignorance if the books are cooked; they are legally responsible for their accuracy.
This law created strict internal controls for how financial data is handled. It requires regular, independent audits and forces companies to be upfront about any weaknesses in their control systems. For any publicly traded company, SOX compliance isn't just a good idea—it's woven into its operational DNA.
The New Frontier: AI and the EU AI Act
Just as the industry got its arms around SOX, a new challenge appeared: artificial intelligence. AI is everywhere now—from algorithmic trading and sophisticated fraud detection to highly personalized loan decisions. This wave of technology brings incredible power, but it also opens up a whole new can of worms when it comes to risk, and regulators are paying close attention.
The EU AI Act is a perfect example of this next layer of oversight. It labels many financial AI applications as ‘high-risk’, which puts them under a much more powerful magnifying glass. This isn't just a bureaucratic label; it reflects the real-world impact these systems can have on people's financial lives.
Imagine an AI system designed to approve or deny mortgage applications. If that model has an unintentional bias in its training data, it could start systematically discriminating against qualified people from a certain neighborhood or background. The EU AI Act tackles this head-on by setting strict new rules for these high-risk systems:
- Rigorous Risk Management: Firms have to constantly assess and manage the risks their AI systems pose, from development to retirement.
- High-Quality Data Sets: The data used to train the AI must be relevant, accurate, and, most importantly, free from biases that could lead to unfair outcomes.
- Human Oversight: A human must always be in the loop. Someone needs to be able to monitor the AI's decisions and step in to override them if things go sideways.
- Complete Transparency: People need to know when they're dealing with an AI, and companies must keep detailed technical records ready for auditors to inspect.
For financial firms, this adds a challenging new dimension to an already demanding compliance load. Building an AI tool is no longer just a coding project; it's a profound regulatory exercise that's changing the very nature of innovation in finance.
Protecting Patients and Data in Healthcare
In healthcare, compliance isn't just a business obligation—it's a human one. The stakes are incredibly high, touching on life-or-death decisions and the most sensitive information a person has. It's no surprise, then, that compliance regulations by industry are at their most stringent here, focusing on two non-negotiable pillars: patient safety and the absolute privacy of personal health data.
This high-stakes environment means there's simply no room for error. A mistake in a pharmaceutical manufacturing line could endanger thousands. A single data breach could expose deeply private medical histories, leading to everything from public shame to professional discrimination. Every single rule exists to build a fortress of trust around the patient.
HIPAA: The Digital Vault for Health Information
When you think about data protection in U.S. healthcare, you're almost certainly thinking of the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). It’s a household name for a reason—it impacts nearly everyone. At its core, HIPAA sets the national standards for keeping protected health information (PHI) safe.
It's helpful to think of HIPAA as the blueprint for a digital vault. It doesn't just demand a strong lock on the door. It dictates who gets a key, requires a detailed log of everyone who enters, and spells out exactly how the contents inside can be handled. Since its passage in 1996, every healthcare provider, insurer, and business partner handling PHI has been required to build robust controls to keep that data confidential. And yet, studies consistently show the healthcare sector still has a long way to go to achieve full compliance.
FDA Oversight: From Lab Bench to Pharmacy Shelf
Beyond data, patient safety comes down to the quality of the medicines and devices themselves. This is the domain of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). The FDA’s rules are exhaustive, governing the entire lifecycle of a medical product—from the earliest research and development phases through clinical trials, manufacturing, and eventually, marketing.
The compliance lift here is massive. Companies must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to guarantee every product is consistent and safe, keep meticulous records for traceability, and report any adverse patient events immediately. Getting a new drug approved is a marathon of regulatory hurdles, each one designed to prove the product is both safe and effective.
The New Era of AI in Medicine and the EU AI Act
Artificial intelligence is changing the face of medicine, bringing incredible potential for everything from detecting diseases earlier to crafting personalized treatment plans. AI algorithms can spot patterns in medical images that the human eye might miss or predict patient outcomes by sifting through mountains of data. But with this incredible power comes significant risk—and regulators are paying close attention.
The EU AI Act tackles this head-on by classifying many medical AI systems as ‘high-risk.’ This isn't just a label; it’s a trigger for a whole new set of stringent compliance duties.
An AI diagnostic tool that misreads a scan, or a treatment algorithm that suggests the wrong therapy, could have devastating consequences. The EU AI Act's 'high-risk' classification exists to prevent such outcomes by enforcing strict oversight.
For the developers building these tools and the healthcare providers using them, complying with the AI Act introduces a demanding new set of requirements. The goal is to make sure the technology is trustworthy, transparent, and fundamentally safe for use with patients.
Here’s what that looks like in practice for high-risk medical AI:
- Data Quality and Governance: The datasets used to train medical AI must be high-quality, relevant, and stripped of biases that could lead to unfair or inaccurate results.
- Human Oversight: A qualified professional must always be in the loop, able to monitor, interpret, and, if needed, override the AI’s suggestions. The final call always rests with a human expert.
- Technical Documentation and Transparency: Organizations have to maintain detailed records on how the AI system was built and how it works, ready for regulators to inspect at any time.
- Robustness and Accuracy: The AI must perform reliably and accurately. This means having clear metrics to prove its effectiveness and solid safety protocols to manage any potential failures.
Wading through these new rules adds another complex layer to an already heavily regulated field. For any healthcare organization, bringing AI into the fold is no longer just a technology decision—it’s a profound compliance challenge.
The New Regulatory Frontier for the Tech Industry
The tech industry is in a unique position. While other sectors are learning how to use AI, tech companies are the ones building it. This puts them right at the epicenter of a regulatory earthquake. The rulebook for the digital world is being rewritten in real-time, moving far beyond simple content moderation to scrutinize the very building blocks of artificial intelligence.
For the creators of this technology, navigating these new compliance regulations by industry isn’t just about following rules—it’s about having a hand in shaping the future responsibly.
This represents a massive shift. Not long ago, tech regulation mostly focused on the aftermath, like data privacy under GDPR. Now, new laws are targeting the creation process itself, putting the algorithms and models that run our digital lives under a microscope. The biggest player on this new field is the landmark EU AI Act, a piece of legislation that's already setting a global benchmark for how AI is governed from the ground up.
Decoding the EU AI Act with the Traffic Light Analogy
The EU AI Act is smart about its approach; it avoids a clumsy, one-size-fits-all solution. Instead, it uses a risk-based framework that’s easy to grasp with a simple traffic light analogy. This system sorts AI applications into different tiers, with the rules getting tougher as the potential for harm goes up. It's a pragmatic way to regulate a complex technology without killing innovation.
This chart helps visualize how compliance costs stack up across different sectors, highlighting why industry-specific rules are so vital.
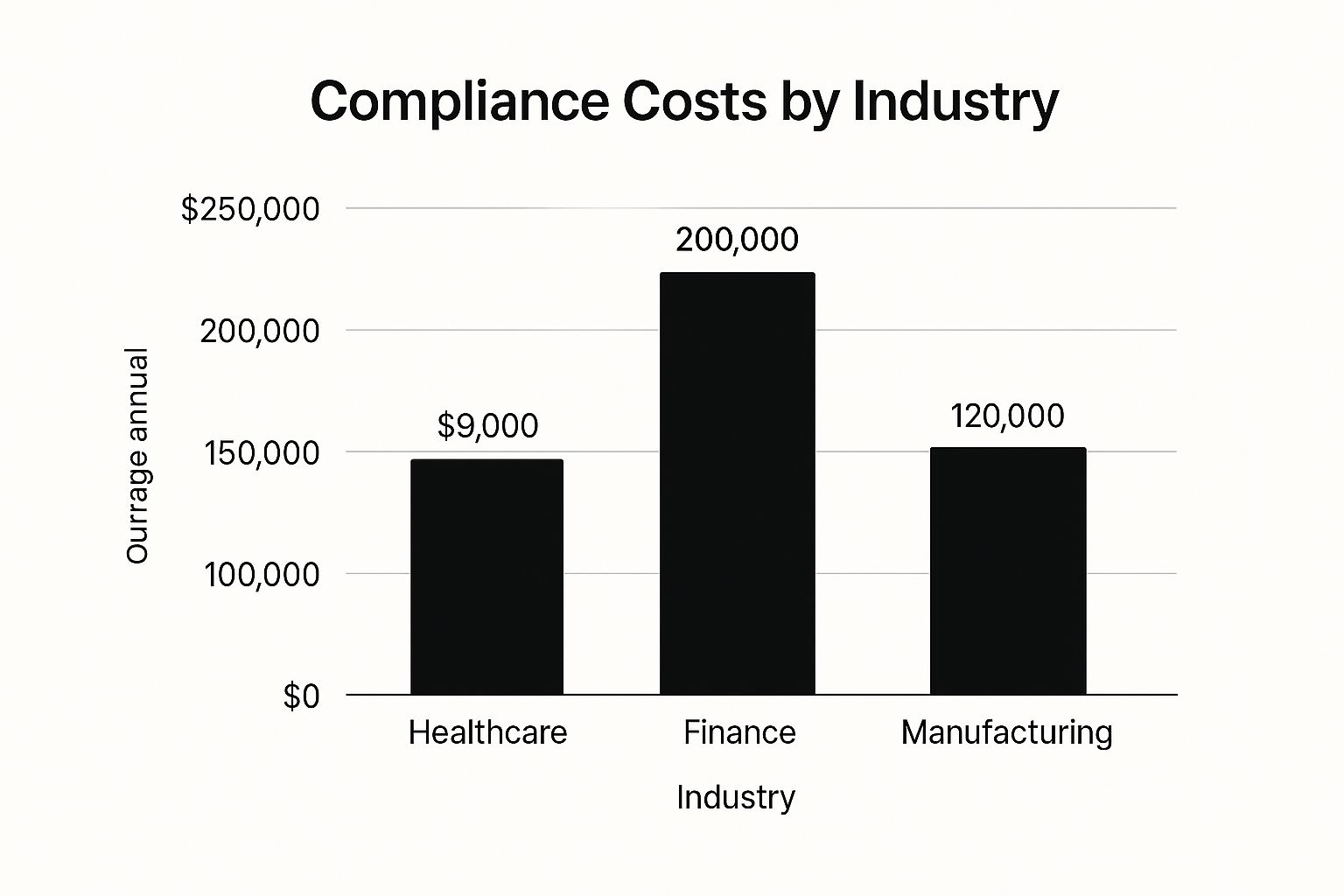
As you can see, finance and healthcare are already grappling with high compliance burdens. With new AI regulations taking full effect, the tech industry's costs are on a steep upward trajectory.
Let's break down the Act's main tiers:
- Red Light (Unacceptable Risk): These are AI systems considered a clear threat to people's safety and fundamental rights. Think government-run social scoring or real-time biometric surveillance in public places. These applications are simply banned.
- Yellow Light (High-Risk): This is where most of the regulatory action is. High-risk systems are those with the potential to seriously impact someone's life or safety. Many common tech tools—like AI used in hiring or social media algorithms that decide what you see—fall right into this category.
- Green Light (Minimal Risk): The vast majority of AI systems, like spam filters or the AI in video games, land here. They just need to be transparent and let users know they're interacting with an AI. Beyond that, there aren't many other strings attached.
This tiered system ensures the tightest controls are saved for the applications that matter most, a core idea you can explore in this detailed guide on the EU Artificial Intelligence Act.
To make this clearer, let's look at how these risk levels apply to a few different industries. The EU AI Act's risk-based approach means a technology that's low-risk in one context could be high-risk in another.
EU AI Act Risk Levels and Industry Examples
| Risk Level | Description | Industry Example (Finance) | Industry Example (Healthcare) | Industry Example (Tech) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unacceptable | Banned due to clear threats to safety and rights. | AI for manipulative "social scoring" to determine creditworthiness. | AI that exploits vulnerabilities of a specific group for harmful purposes. | Real-time remote biometric identification in public spaces. |
| High | Requires strict compliance, documentation, and oversight. | AI systems used for credit scoring and loan application assessments. | AI-powered diagnostic tools or software for robotic surgery. | AI algorithms used in recruitment software or for content moderation. |
| Limited | Requires basic transparency obligations. | Chatbots for customer service that must identify themselves as AI. | AI-driven wellness apps that generate personalized advice. | Deepfake generation tools must disclose that the content is artificial. |
| Minimal | No specific legal obligations, voluntary codes of conduct. | AI used for internal fraud detection pattern analysis. | AI systems that help manage hospital administrative schedules. | AI-powered spam filters or recommendation engines in video games. |
This table shows just how context-dependent AI regulation is. The same underlying technology can face drastically different rules depending on its application.
New Obligations for Tech Creators
For tech companies building anything classified as high-risk, the EU AI Act rolls out a demanding list of new responsibilities. These aren't just suggestions; they are legally binding duties designed to guarantee safety, fairness, and transparency across the entire AI lifecycle. It’s no longer good enough to just ship a working product. Now, companies have to prove it's safe and equitable before it ever hits the market.
A core change under the AI Act is that the burden of proof has shifted to the developer. It's now on you to show your high-risk AI is trustworthy, not on regulators to prove it's harmful.
This proactive requirement forces a total rethink of internal governance. Tech companies must now weave compliance deep into their development DNA.
The main duties for high-risk systems include:
- Conformity Assessments: Before a high-risk AI can be sold in the EU, it has to pass a tough assessment to prove it meets the Act's standards for risk management, data quality, and human oversight.
- Technical Documentation: Companies need to keep detailed records explaining how the AI was built, trained, and tested. This documentation has to be kept current and be ready for regulators to inspect at any time.
- Post-Market Monitoring: The job isn’t done at launch. Developers are on the hook for continuously monitoring how their AI performs in the real world and must report any serious incidents or failures to the authorities.
These rules mark a completely new frontier for tech governance. They are pushing the industry toward a model where safety and ethics are no longer afterthoughts but are central to the innovation process itself, setting a powerful new standard for the rest of the world.
Building a Future-Proof Compliance Strategy

Knowing the current compliance regulations by industry is a great start, but it’s only half the battle. The rulebook is constantly being rewritten, especially with new technologies like AI forcing everyone to rethink what risk and responsibility even mean. A reactive, check-the-box mentality just doesn't cut it anymore—it leaves you permanently playing catch-up.
To actually get ahead, you have to shift from periodic audits to a state of continuous compliance. Think of it like this: a smoke alarm is great, but it only goes off after a fire starts. A full-time fire marshal, on the other hand, is always on-site, monitoring conditions to prevent a fire from ever breaking out in the first place. That’s the difference.
This proactive mindset is becoming the new standard. In fact, 82% of companies are planning to spend more on compliance tech to handle this growing complexity. By mid-2025, 56% of enterprises expect to have moved their compliance systems to the cloud, and a whopping 91% of companies are aiming for a continuous compliance model within five years. The writing is on the wall, as these 25 critical compliance stats on complianceandrisks.com show.
Adopting Proactive Compliance Technologies
This move toward continuous compliance is really being driven by new tools. AI-powered platforms and cloud-based systems give you real-time monitoring and automated alerts, plus the flexibility to adapt to new rules like the EU AI Act as they roll out. These tools don't just help you spot problems faster; they can actually help predict where the next risks might pop up.
Modern compliance isn't just a cost center; it's a strategic advantage. It builds the kind of deep customer trust and operational resilience that sets market leaders apart from the rest of the pack.
Investing in the right software for compliance is a foundational step. The right platform can pull all your regulatory data into one place, automate how you gather evidence, and give auditors a single, reliable source of truth. It turns what is often a chaotic scramble into a well-managed process.
Essential Best Practices for Your Strategy
Of course, technology isn't a silver bullet. A truly future-proof strategy needs a solid bedrock of smart policies and well-trained people. It’s about weaving compliance into the fabric of your company culture, not just bolting it onto your IT stack.
To build a framework that can withstand whatever comes next, focus on these core practices:
- Conduct Regular Risk Assessments: This is your early warning system. Proactively search for potential gaps, especially around new technologies or changes in how you do business.
- Invest in Continuous Employee Training: Your team is your first and best line of defense. Make sure everyone, from the top down, understands their responsibilities, from handling data properly to using AI tools ethically.
- Establish a Clear AI Governance Framework: With laws like the EU AI Act on the horizon, you absolutely need clear, internal rules for how you develop, deploy, and monitor AI. This framework should spell out who is accountable, demand transparency, and ensure human oversight.
- Maintain an Audit-Ready Posture: Keep your documentation organized and current at all times. When you use a central platform, pulling reports and answering auditor questions becomes a routine task, not a frantic, last-minute fire drill.
By combining the right tech with these fundamental practices, you can finally shift compliance from a reactive headache to a proactive strength. This isn't just about avoiding fines; it's about building a more trustworthy, resilient business that’s ready for the future.
Common Compliance Questions Answered
When you're trying to get a handle on industry-specific regulations, the same questions tend to pop up again and again. It's totally normal. Let's tackle some of the most frequent ones I hear, especially with big new rules like the EU AI Act making waves.
How Does the EU AI Act Affect Companies Outside the EU?
This is a big one, and it catches a lot of people by surprise. The EU AI Act has what's called extraterritorial reach.
In simple terms, it doesn't matter where your company is based. If you're putting an AI system on the market in the European Union, or even if the output of your AI system is used there, you fall under its rules. Think of a US-based software company selling its AI-powered analytics tool to a client in Germany—that company absolutely has to comply with the Act.
What Is the Biggest Compliance Hurdle for Small Businesses?
For smaller businesses, it almost always comes down to one thing: limited resources.
Juggling complex regulations takes a ton of specialized knowledge, not to mention the budget for the right technology and people. It can feel overwhelming. The smartest way forward is to focus on the biggest risks first, like data privacy, and look for scalable, cloud-based compliance tools that can do some of the heavy lifting without breaking the bank.
You'll notice that ESG and financial compliance are starting to blend together more and more. It's not just a trend. Regulators are now forcing financial institutions to report on climate-related financial risks. At the same time, ESG criteria are becoming central to investment decisions, which means a company's environmental track record can directly affect its ability to secure funding.
Ready to master EU AI Act compliance? ComplyACT AI guarantees your organization is audit-ready in just 30 minutes, helping you avoid massive fines and build a foundation of trust. Learn more about ComplyACT AI.